Biography
Mazen Soufi is an assistant professor of information science at Imaging-based Computational Biomedicine lab in Nara Institute of Science and Technology (NAIST). My research focuses on the analysis of disease progression trends based on features dervied from multi-modality medical images (such as MRI, CT or histopathology images). In my work, I use deep learning-based image segmentation algorithms to extract the target organs/structures and perform downstream analysis.
I worked before in projects involving range image-based approaches for monitoring head and neck cancer patients during raditation therapy, prognostic prediction of lung cancer patients using CT image features, and liver fibrosis grading in MR images based on statistical shape analysis. I’m currently interested in the analysis of musculoskeletal (MSK) structures to have insights into the age- and disease-related variations. To pursue this goal, I collaborate with multiple healthcare/medical institutions in Japan and abroad to analyze large-scale (x10,000s volumetric images) databases. I finally aim at developing novel image biomarkers to be used in improving our understanding of aging and disease of the MSK system.
I primiarly use python and the mainstream deep learning frameworks (Tensorflow, PyTorch, MONAI) with the main medical image analysis and visualization libraries (VTK, ITK, Elastix) in my reseach.
Besides my research, I serve as a reviewer for multiple journals and conferences (domestic and international), including MICCAI, Heliyon (Cell), Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics, ITE Transactions on Media Technology and Applications, and Advanced Biomedical Engineering.
- Medical Imaging
- Artificial Intelligence & Deep Learning
- Disease Progression & Large-Scale Data Analysis
-
PhD (Health Sciences), 2017
Kyushu University, Japan
-
Master's Degree (Health Sciences), 2014
Kyushu University, Japan
-
BSc (Biomedical Engineering), 2011
Damascus University, Syria
Experience
Responsibilities include:
- Master/PhD course student research mentorship
- Research and development: multiple projects involving MRI, CT and histopathology image analysis
- Teaching
- Lab environment administration (GPU cluster “slurm+singularity” and data servers “Windows Server, NAS”, Fujifilm Vincent workstaion)
- Operation of standing MRI scanner (E-MRI Brio G-Scan, Esaote) for image acquisition
Featured Publications
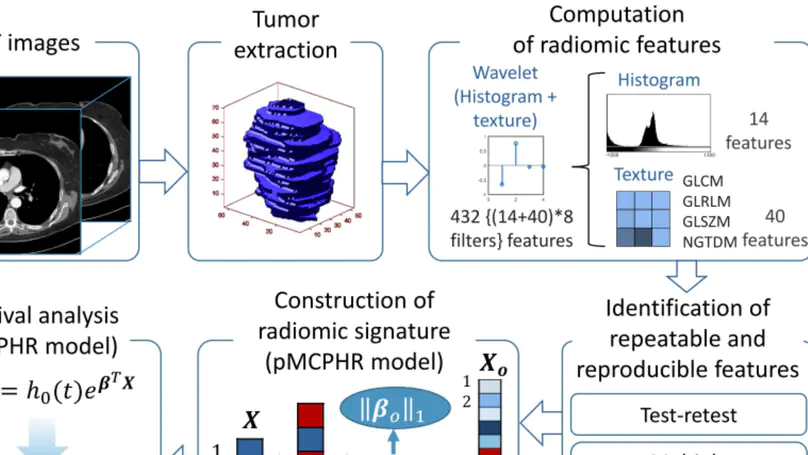
Artificial intelligence (AI) technologies have enabled precise three-dimensional analysis of individual muscles on computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance images via automatic segmentation. This study aimed to perform three-dimensional assessments of pelvic and thigh muscle atrophy and fatty degeneration in patients with unilateral hip osteoarthritis using CT and to evaluate the correlation with health-related quality of life (HRQoL).
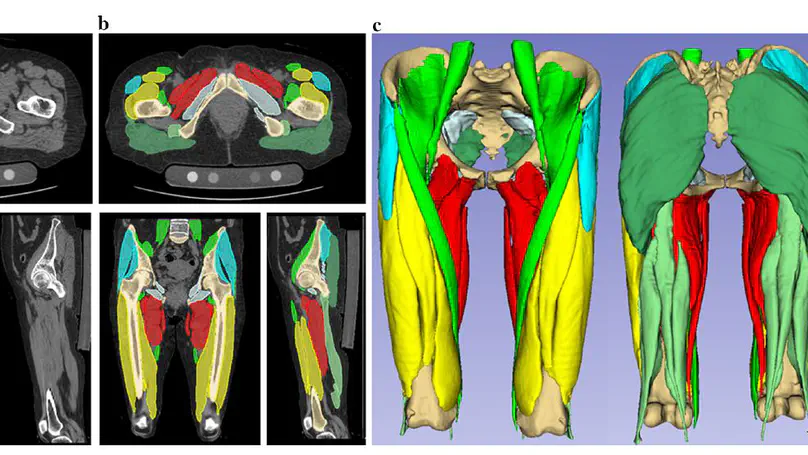
The use of deep learning (DL) in medical imaging is becoming increasingly widespread. Although DL has been used previously for the segmentation of facial bones in computed tomography (CT) images, there are few reports of segmentation involving multiple areas. In this study, a U-Net was used to investigate the automatic segmentation of facial bones into eight areas, with the aim of facilitating virtual surgical planning (VSP) and computer-aided design and manufacturing (CAD/CAM) in maxillofacial surgery. CT data from 50 patients were prepared and used for training, and five-fold cross-validation was performed. The output results generated by the DL model were validated by Dice coefficient and average symmetric surface distance (ASSD). The automatic segmentation was successful in all cases, with a mean± standard deviation Dice coefficient of 0.897 ± 0.077 and ASSD of 1.168 ± 1.962 mm. The accuracy was very high for the mandible (Dice coefficient 0.984, ASSD 0.324 mm) and zygomatic bones (Dice coefficient 0.931, ASSD 0.487 mm), and these could be introduced for VSP and CAD/CAM without any modification. The results for other areas, particularly the teeth, were slightly inferior, with possible reasons being the effects of defects, bonded maxillary and mandibular teeth, and metal artefacts. A limitation of this study is that the data were from a single institution. Hence further research is required to improve the accuracy for some facial areas and to validate the results in larger and more diverse populations.
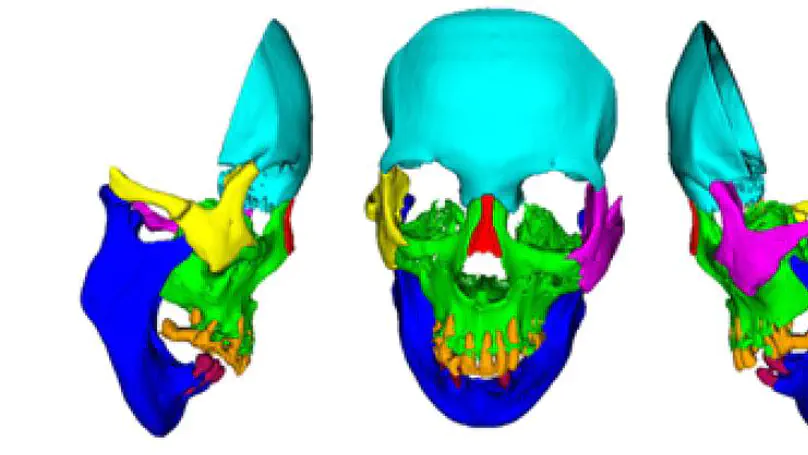
Purpose In quantitative computed tomography (CT), manual selection of the intensity calibration phantom’s region of interest is necessary for calculating density (mg/cm3) from the radiodensity values (Hounsfield units HU). However, as this manual process requires effort and time, the purposes of this study were to develop a system that applies a convolutional neural network (CNN) to automatically segment intensity calibration phantom regions in CT images and to test the system in a large cohort to evaluate its robustness. Methods This cross-sectional, retrospective study included 1040 cases (520 each from two institutions) in which an intensity calibration phantom (B-MAS200, Kyoto Kagaku, Kyoto, Japan) was used. A training dataset was created by manually segmenting the phantom regions for 40 cases (20 cases for each institution). The CNN model’s segmentation accuracy was assessed with the Dice coefficient, and the average symmetric surface distance was assessed through fourfold cross-validation. Further, absolute difference of HU was compared between manually and automatically segmented regions. The system was tested on the remaining 1000 cases. For each institution, linear regression was applied to calculate the correlation coefficients between HU and phantom density. Results The source code and the model used for phantom segmentation can be accessed at https://github.com/keisuke-uemura/CT-Intensity-Calibration-Phantom-Segmentation. The median Dice coefficient was 0.977, and the median average symmetric surface distance was 0.116 mm. The median absolute difference of the segmented regions between manual and automated segmentation was 0.114 HU. For the test cases, the median correlation coefficients were 0.9998 and 0.999 for the two institutions, with a minimum value of 0.9863. Conclusion The proposed CNN model successfully segmented the calibration phantom regions in CT images with excellent accuracy.
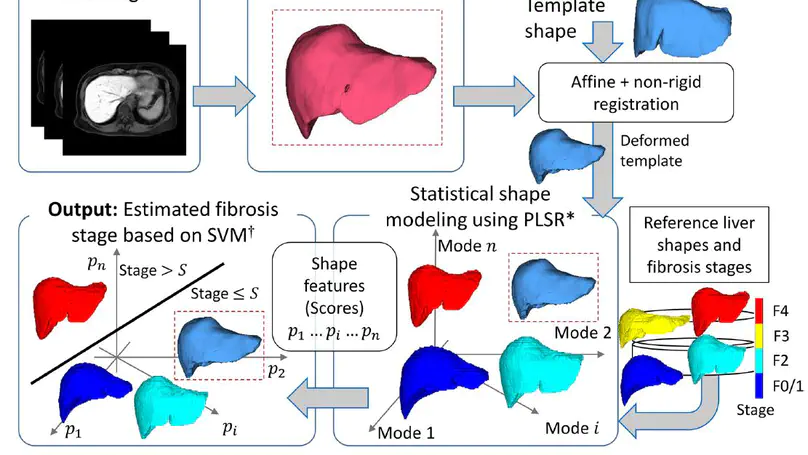
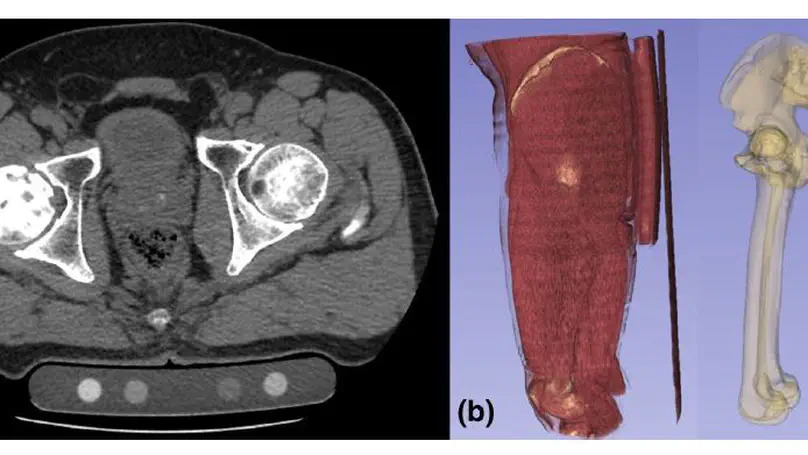
An application of a statistical shape modelling approach using partial least squares regression (PLSR), which explicitly uses the stage as supervised information, for understanding the shape variations associated with the stage as well as predicting it in contrast-enhanced MR images.
Recent Publications
Contact
- msoufi [at] is.naist.jp
- 8916-5 Takayama-cho, Ikoma, 630-0192
- Information Science Bld B, F5, B502